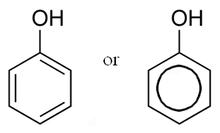
Phenol is a highly toxic compound, which is one of the priority
pollutants listed by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Thus,
water bodies require to be properly treated prior to being discharged. For
biodegradation of phenol, two vertically rotating immobilized reactor was
constructed. It was observed that the
efficacy of phenol degradation was high unaccompanied with the production of
secondary by-products.
Materials and
Methods:
Microorganisms:
The
phenol-degrading A. lwoffii accession number KM985371 and the surfactin
producing B. subtilis strain BDCC-TUSA-3 were used.
Chemicals and
culture media: All chemicals used were analytical reagents. The minimal salt
media (MSM) was used in present study. It contained KH2PO4 0.5 g, K2HPO4 0.5 g,
CaCl2 0.1 g, NaCl 0.2 g, MgSO4.7H2O 0.5 g, MnSO4.7H2O 0.01 g, FeSO2.7H2O 0.01
g, NH4NO3 1.0 g per liter. Deionized, distilled water was used for the
experiments. The activated sludge samples were collected in a biological
treatment system, Jeddah refinery, KSA. Read more>>>>>>>>>>>>
Comments
Post a Comment